Amplifier Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to electronic circuits, the amplifier op amp, or operational amplifier, is a cornerstone component. It’s a versatile device that can be used in a wide range of applications, from basic signal conditioning to complex signal processing. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the amplifier op amp, exploring its features, applications, and how to use it effectively.
Understanding the Basics

The amplifier op amp is an electronic device that amplifies voltage signals. It consists of a differential input stage, a voltage amplifier stage, and an output stage. The differential input stage allows the op amp to amplify the difference between two input voltages, making it highly sensitive to small changes in voltage. The voltage amplifier stage increases the voltage level, and the output stage drives the load, which could be another circuit or a device like a speaker.
One of the key characteristics of the amplifier op amp is its high input impedance and low output impedance. This means that it draws very little current from the input signal and can drive loads with varying impedance levels. The high input impedance also makes it suitable for use with high-impedance sources, such as thermocouples and photodiodes.
Types of Amplifier Op Amps

There are several types of amplifier op amps, each with its own set of features and applications. Here are some of the most common types:
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| CMOS Op Amp | Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor operational amplifier | Low power, high input impedance, and low noise applications |
| Bipolar Op Amp | Operational amplifier with bipolar transistors | High precision, high gain, and high bandwidth applications |
| Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA) | Operational amplifier with a transconductance output | Audio amplification, signal processing, and control applications |
How to Use an Amplifier Op Amp
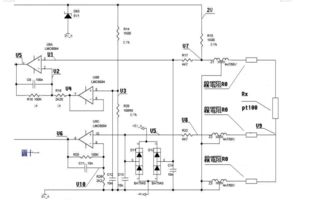
Using an amplifier op amp in a circuit is relatively straightforward. Here are the basic steps:
- Choose the appropriate op amp for your application based on its specifications, such as input impedance, output impedance, gain, and bandwidth.
- Connect the input signal to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (-) inputs of the op amp. The non-inverting input has a higher input impedance, making it more suitable for high-impedance sources.
- Connect the output of the op amp to the load, which could be another circuit or a device like a speaker.
- Adjust the gain of the op amp using a feedback resistor network. The gain is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor to the input resistor.
- Power the op amp using a suitable power supply, ensuring that the voltage levels are within the specified range.
Applications of Amplifier Op Amps
Amplifier op amps are used in a wide range of applications, including:
-
Signal conditioning: Amplifying, filtering, and shaping signals for further processing or transmission.
-
Control systems: Implementing feedback loops and other control algorithms to regulate the behavior of a system.
-
Audio amplification: Boosting the volume of audio signals for speakers and headphones.
-
Instrumentation: Measuring and processing signals from sensors and transducers.
-
Data acquisition: Converting analog signals to digital signals for processing by a computer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the amplifier op amp is a powerful and versatile component that plays a crucial role in electronic circuits. By understanding its basics, types, and applications, you can effectively use it to design and implement a wide range of electronic systems.








