Understanding the Bandwidth of Op Amp Formula: A Detailed Guide
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), one of the most crucial parameters to consider is the bandwidth. The bandwidth of an op-amp refers to the range of frequencies over which the amplifier can operate effectively. In this article, we will delve into the formula for calculating the bandwidth of an op-amp and explore its significance in various applications.
What is Bandwidth?
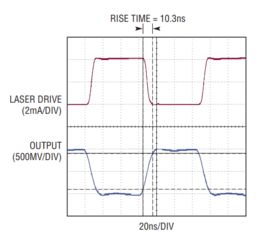
The bandwidth of an op-amp is defined as the frequency range over which the gain of the amplifier remains within a certain percentage of its maximum value. Typically, this percentage is 70.7% or -3dB of the maximum gain. Understanding the bandwidth is essential because it determines the frequency response of the op-amp and its suitability for specific applications.
The Bandwidth Formula
The formula for calculating the bandwidth of an op-amp is relatively straightforward. It is given by:
BW = GBW / Aol
Where:
- BW is the bandwidth in hertz (Hz)
- GBW is the gain-bandwidth product in hertz (Hz)
- Aol is the open-loop gain of the op-amp
The gain-bandwidth product (GBW) is a characteristic of the op-amp and is typically provided in the datasheet. The open-loop gain (Aol) is the gain of the op-amp when no feedback is applied. It is also provided in the datasheet.
Calculating Bandwidth

Let’s consider an example to illustrate how to calculate the bandwidth of an op-amp. Suppose we have an op-amp with a GBW of 10 MHz and an open-loop gain of 100,000. Using the formula, we can calculate the bandwidth as follows:
BW = 10 MHz / 100,000 = 100 Hz
This means that the op-amp can operate effectively over a frequency range of 100 Hz to 10 MHz, as long as the gain remains within 70.7% of its maximum value.
Significance of Bandwidth
The bandwidth of an op-amp is crucial for several reasons:
- Frequency Response: The bandwidth determines the frequency response of the op-amp, which is essential for applications such as filtering, signal processing, and communication systems.
- Distortion: A wider bandwidth generally results in lower distortion, which is important for audio and video applications.
- Stability: The bandwidth affects the stability of the op-amp, especially when used in feedback configurations. A higher bandwidth can lead to instability if not properly compensated.
Applications of Bandwidth
The bandwidth of an op-amp is essential in various applications, including:
- Audio Amplifiers: The bandwidth determines the frequency range of the audio signal that can be amplified without significant distortion.
- Filter Design: The bandwidth is crucial for designing filters that can effectively remove unwanted frequencies from a signal.
- Communication Systems: The bandwidth determines the frequency range over which the op-amp can operate effectively in communication systems, such as wireless and wired networks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the bandwidth of an op-amp is a critical parameter that determines its frequency response and suitability for various applications. By understanding the bandwidth formula and its significance, you can make informed decisions when selecting an op-amp for your specific needs.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth | The frequency range over which the gain of the op-amp remains within a certain percentage of its maximum value. |
| Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW) | A characteristic of the op-amp that determines its bandwidth and is typically provided in the datasheet. |
| Open-Loop Gain (Aol) | The gain of the op-amp when no feedback is applied and is also provided in
|






