Understanding Op Amp Level Shifter: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to interfacing different voltage levels in electronic circuits, an Op Amp Level Shifter plays a crucial role. This device ensures that signals are correctly translated and transmitted between different voltage domains. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Op Amp Level Shifters, exploring their working principles, applications, and design considerations.
What is an Op Amp Level Shifter?

An Op Amp Level Shifter is an electronic circuit that converts a signal from one voltage level to another. It is commonly used in digital circuits to interface devices with different voltage levels, such as TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor). The primary function of an Op Amp Level Shifter is to ensure that the signal remains intact during the conversion process.
Working Principle of an Op Amp Level Shifter
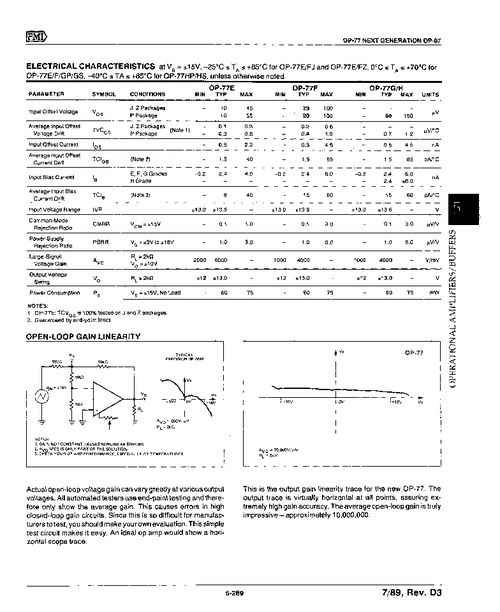
The working principle of an Op Amp Level Shifter is based on the non-inverting amplifier configuration. The circuit typically consists of an operational amplifier (Op Amp), a voltage reference, and a feedback resistor network. The input signal is applied to the non-inverting input of the Op Amp, while the inverting input is connected to the voltage reference. The output of the Op Amp is then taken from the output terminal, which provides the converted signal.
When the input signal is applied to the non-inverting input, the Op Amp amplifies the signal and adds a voltage offset determined by the voltage reference. The feedback resistor network ensures that the output signal is correctly translated to the desired voltage level. The amplification factor and voltage offset can be adjusted by modifying the values of the resistors in the circuit.
Applications of Op Amp Level Shifters

Op Amp Level Shifters find applications in various electronic systems, including:
-
Interfacing TTL and CMOS circuits
-
Connecting microcontrollers with different voltage levels
-
Transmitting signals across voltage domains in mixed-signal circuits
-
Driving high-impedance loads
Design Considerations for Op Amp Level Shifters
When designing an Op Amp Level Shifter, several factors need to be considered:
-
Input and output voltage levels: Ensure that the Op Amp Level Shifter can handle the voltage levels of the input and output signals.
-
Signal integrity: The circuit should maintain the signal integrity during the conversion process, minimizing distortion and noise.
-
Power consumption: Design the circuit to minimize power consumption, especially in battery-powered applications.
-
Speed: The Op Amp Level Shifter should be capable of handling high-speed signals without introducing significant delays.
Types of Op Amp Level Shifters
There are several types of Op Amp Level Shifters, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
-
Single-supply Op Amp Level Shifter: This type of level shifter operates with a single supply voltage and is suitable for interfacing TTL and CMOS circuits.
-
Split-supply Op Amp Level Shifter: This type of level shifter operates with two supply voltages and is suitable for interfacing circuits with different voltage levels.
-
Bus-level Op Amp Level Shifter: This type of level shifter is designed to handle high-speed signals and is commonly used in bus interfacing applications.
Comparison of Op Amp Level Shifters
Below is a comparison table of different Op Amp Level Shifters based on their key specifications:
| Op Amp Level Shifter | Supply Voltage | Speed | Power Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-supply Op Amp Level Shifter | Single supply voltage | Medium | Low |
| Split-supply Op Amp Level Shifter | Two supply voltages | High | Medium |







