Op Amp Bandwidth Limiting: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the concept of bandwidth limiting in operational amplifiers (op-amps) is crucial for anyone working in the field of electronics. Bandwidth limiting, also known as frequency compensation, is a technique used to control the frequency response of an op-amp. By doing so, it ensures stable operation and prevents unwanted oscillations. In this article, we will delve into the details of op amp bandwidth limiting, exploring its significance, implementation, and various aspects that affect its performance.
What is Bandwidth Limiting?

Bandwidth limiting refers to the process of restricting the frequency range over which an op-amp operates. This is achieved by introducing a frequency-dependent component, such as a capacitor or resistor, into the feedback loop of the op-amp. The purpose of bandwidth limiting is to ensure that the op-amp remains stable and maintains a desired frequency response.
Why is Bandwidth Limiting Necessary?

Op-amps are designed to amplify signals over a wide frequency range. However, in certain applications, it is necessary to limit the bandwidth to prevent unwanted oscillations, reduce noise, or achieve a specific frequency response. Bandwidth limiting helps in achieving these objectives by controlling the gain of the op-amp at higher frequencies.
Types of Bandwidth Limiting Techniques
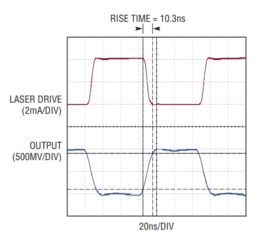
There are several techniques used for bandwidth limiting in op-amps. The most common ones are:
-
Shunt Compensation: This technique involves adding a capacitor in parallel with the feedback resistor. The capacitor provides a low-impedance path at higher frequencies, effectively reducing the gain of the op-amp.
-
Series Compensation: In this technique, a resistor is added in series with the feedback resistor. The resistor provides a high-impedance path at higher frequencies, which also reduces the gain of the op-amp.
-
Parallel Compensation: This technique involves adding a capacitor in parallel with the feedback resistor and a resistor in series with the capacitor. This combination provides a controlled frequency response and reduces the gain at higher frequencies.
Implementation of Bandwidth Limiting
Implementing bandwidth limiting in an op-amp circuit involves selecting the appropriate compensation technique and component values. The following table provides a comparison of the three common techniques:
| Technique | Component | Effect on Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Shunt Compensation | Capacitor | Reduces gain at higher frequencies |
| Series Compensation | Resistor | Reduces gain at higher frequencies |
| Parallel Compensation | Capacitor and Resistor | Reduces gain at higher frequencies |
When selecting the component values, it is essential to consider the desired bandwidth and the frequency response of the op-amp. The following formula can be used to calculate the cutoff frequency (fc) for shunt compensation:
fc = 1 / (2 蟺 Rf Cf)
where Rf is the feedback resistor and Cf is the capacitor value.
Effects of Bandwidth Limiting
Bandwidth limiting has several effects on the performance of an op-amp:
-
Stability: By limiting the bandwidth, the op-amp becomes more stable and less prone to oscillations.
-
Frequency Response: Bandwidth limiting helps in achieving a desired frequency response by controlling the gain at higher frequencies.
-
Noise Reduction: Limiting the bandwidth can reduce noise at higher frequencies, resulting in a cleaner output signal.
Conclusion
Op amp bandwidth limiting is a crucial technique for ensuring stable and reliable operation of op-amps in various applications. By understanding the different compensation techniques and their effects, you can design circuits that meet your specific requirements. Remember to carefully select the component values and consider the desired bandwidth and frequency response when implementing bandwidth limiting in your circuits.




