Data Ops: A Comprehensive Guide
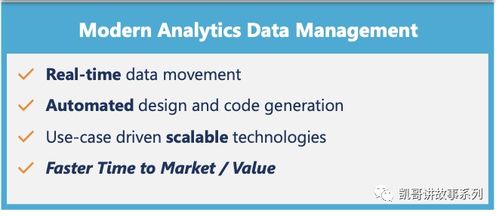
Data Ops, short for Data Operations, is a relatively new concept in the world of data management. It focuses on creating a seamless and efficient data pipeline that enables quick and flexible data services for users. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of Data Ops, including its definition, benefits, key components, and real-world applications.
Understanding Data Ops
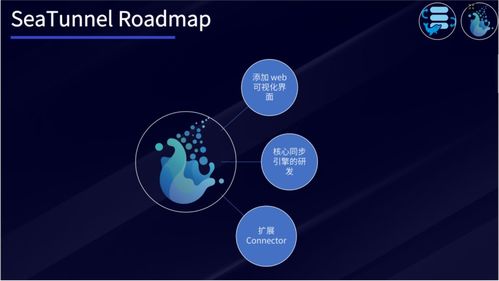
Data Ops is not a specific technology, product, or platform. Instead, it is a strategy or methodology that operates on top of data platforms, data centers, and data lakes. It aims to bridge the gap between data engineers and data consumers by ensuring that data is easily accessible, reliable, and secure.
According to鍌呬竴骞宠€佸笀, Data Ops can be considered as the foundation of a data platform, or what he calls the “ability base” of a data center. Its primary goal is to enable the rapid development and deployment of data services, thereby promoting data sharing and reuse.
Key Components of Data Ops
Data Ops encompasses several key components that work together to create a robust and efficient data pipeline. These components include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection and Integration | Automating the process of integrating new data sources and pipelines, preparing, cleaning, and managing data. |
| Continuous Delivery of Trusted Data | Implementing data governance throughout the data pipeline to ensure the delivery of trusted, secure, and compliant data. |
| Enhanced Data Services | Deploying data-driven applications that provide real-time insights and recommendations to users. |
Data Collection and Integration
This component involves automating the process of integrating new data sources and pipelines. It includes tasks such as data preparation, cleaning, and management. By using technologies like Change Data Capture (CDC) and stream processing, data pipelines can be transformed into real-time streams, enabling real-time analytics and interactive applications.
Business users can leverage data catalogs and data preparation tools to discover and automate data workflows, making data more accessible and convenient to use.
Continuous Delivery of Trusted Data
This component focuses on ensuring the delivery of trusted, secure, and compliant data. Data governance is implemented throughout the data pipeline to ensure data quality, security, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
By integrating data governance, data cataloging, data quality, and data privacy into a unified, intelligent data platform, organizations can ensure that all data is trusted and protected.
Enhanced Data Services
This component involves deploying data-driven applications that provide real-time insights and recommendations to users. By monitoring and managing data pipelines using AI and machine learning technologies, organizations can optimize performance and capacity, ensuring that data services are always available and reliable.
Real-World Applications of Data Ops
Data Ops has been successfully implemented in various industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing. Here are some examples of real-world applications:
-
Financial institutions use Data Ops to monitor and analyze trading data in real-time, enabling them to make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
-
Healthcare organizations leverage Data Ops to analyze patient data, identify trends, and improve patient outcomes.
-
Retail companies use Data Ops to analyze customer behavior and preferences, enabling them to personalize marketing campaigns and improve customer satisfaction.
-
Manufacturing companies employ Data Ops to optimize production processes, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
Conclusion
Data Ops is a powerful strategy that helps organizations unlock the full potential of their data. By focusing on creating a seamless and efficient data pipeline, Data Ops enables organizations to make data-driven decisions, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation.







