FET vs BJT Op Amp: A Detailed Multi-Dimensional Comparison
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), the choice between a Field-Effect Transistor (FET) and a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) can significantly impact the performance and functionality of your circuit. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of both FET and BJT op-amps, comparing their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages from various perspectives.
Transistor Type and Operation
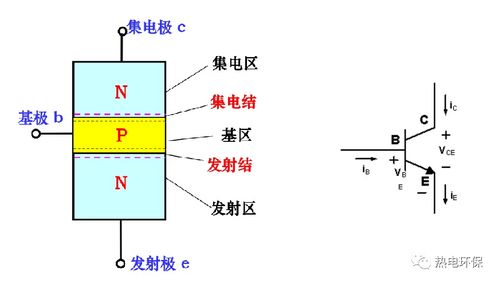
Let’s start by understanding the fundamental differences between FET and BJT transistors. A FET is a voltage-controlled device, meaning its output current is controlled by the voltage applied to its gate terminal. On the other hand, a BJT is a current-controlled device, where the output current is controlled by the base current.
| Parameter | FET | BJT |
|---|---|---|
| Control Mechanism | Voltage-controlled | Current-controlled |
| Input Impedance | High | Low |
| Output Impedance | Low | High |
| Power Consumption | Low | High |
These differences in control mechanism, input impedance, output impedance, and power consumption have a significant impact on the performance of op-amps based on FET and BJT transistors.
Input Impedance and Output Impedance
Input impedance is a crucial factor in op-amps, as it determines how much the input signal is loaded. FET op-amps typically have a high input impedance, which makes them suitable for circuits with high-impedance sources. In contrast, BJT op-amps have a lower input impedance, which can load the input signal more significantly.
Output impedance, on the other hand, determines how much the output signal is loaded. FET op-amps generally have a lower output impedance, making them more suitable for driving loads with low impedance. BJT op-amps, with their higher output impedance, may not be as effective in driving heavy loads.
Power Consumption

Power consumption is another critical factor to consider when choosing between FET and BJT op-amps. FET op-amps are known for their low power consumption, which makes them ideal for battery-powered applications. BJT op-amps, on the other hand, consume more power, which can be a concern in low-power circuits.
Frequency Response
Frequency response is an essential parameter for op-amps, as it determines their ability to amplify signals across a wide range of frequencies. FET op-amps generally have a wider frequency response compared to BJT op-amps, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Temperature Stability
Temperature stability refers to the ability of an op-amp to maintain its performance over a range of temperatures. FET op-amps are known for their excellent temperature stability, which makes them suitable for applications where temperature variations are a concern. BJT op-amps may exhibit more significant performance variations with temperature changes.
Cost and Availability
Cost and availability are also important factors to consider when choosing between FET and BJT op-amps. FET op-amps are generally more expensive than BJT op-amps, but they offer superior performance in many applications. BJT op-amps, being more affordable, are often used in cost-sensitive applications.
In conclusion, the choice between FET and BJT op-amps depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your application. FET op-amps are ideal for high-impedance sources, low-power applications, and high-frequency circuits. BJT op-amps, on the other hand, are more suitable for low-impedance sources, cost-sensitive applications, and circuits with moderate frequency requirements.







