DAC Circuit Using Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) circuit, especially when it incorporates an operational amplifier (op amp), is crucial for anyone delving into the realms of digital signal processing and analog circuit design. By using an op amp in a DAC circuit, you can achieve higher precision, improved linearity, and better overall performance. Let’s explore the intricacies of this fascinating topic.
What is a DAC Circuit?
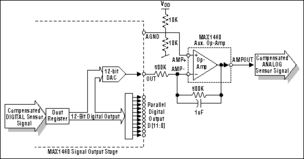
A DAC circuit is an electronic device that converts digital data into an analog signal. This conversion is essential for various applications, such as audio playback, video display, and wireless communication. The primary function of a DAC is to take binary data, represented by a series of 1s and 0s, and convert it into a continuous analog signal that can be easily processed by analog devices.
How Does a DAC Circuit Work?

A DAC circuit typically consists of a resistor ladder network, a reference voltage source, and a digital input. The resistor ladder network is a series of resistors connected in a binary-weighted configuration. The reference voltage source provides a stable voltage reference for the conversion process. The digital input, which can be a binary code, determines the output voltage of the DAC circuit.
When a binary code is applied to the DAC circuit, the corresponding resistors in the ladder network are connected to the output, creating a voltage divider. The output voltage is then proportional to the binary code input. The op amp in the circuit amplifies this output voltage to the desired level, ensuring that the analog signal is strong enough to drive the load.
The Role of Op Amp in a DAC Circuit

An operational amplifier (op amp) is a versatile and powerful electronic component that can be used in various applications, including amplification, filtering, and signal conditioning. In a DAC circuit, the op amp plays a crucial role in improving the performance of the circuit.
One of the primary functions of the op amp in a DAC circuit is to provide a high-impedance input, which ensures that the digital input signal is not affected by the internal resistance of the DAC. This high-impedance input is essential for maintaining the accuracy of the conversion process.
Additionally, the op amp amplifies the output voltage of the DAC circuit, ensuring that the analog signal is strong enough to drive the load. This amplification is crucial for achieving high-fidelity audio playback and other applications that require a strong analog signal.
Types of DAC Circuits Using Op Amps
There are several types of DAC circuits that use op amps, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include:
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Binary-weighted resistor ladder | Consists of resistors with binary-weighted values, providing a linear output voltage | Audio playback, video display, and wireless communication |
| Successive-approximation register (SAR) | Utilizes a comparator and a register to convert digital data into an analog signal | High-speed data conversion, medical equipment, and industrial applications |
| Delta-sigma modulator | Combines a DAC with a sigma-delta modulator to achieve high-resolution conversion | Audio playback, data acquisition, and wireless communication |
Design Considerations for DAC Circuits Using Op Amps
When designing a DAC circuit using an op amp, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance. Some of the key considerations include:
-
Input impedance: The op amp should have a high input impedance to minimize the loading effect on the digital input signal.
-
Output impedance: The op amp should have a low output impedance to drive the load effectively.
-
Bandwidth: The op amp should have a sufficient bandwidth to handle the frequency content of the analog signal.
-
Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR): The op amp should have a high PSRR to minimize the impact of power supply noise on the output signal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a








