Understanding Op Amp Gain: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), one of the most crucial parameters to understand is the gain. The gain of an op-amp determines how much it amplifies the input signal. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of op amp gain, including its definition, types, calculation, and practical applications.
What is Op Amp Gain?

Op amp gain, often denoted as ‘A’, is a measure of how much an op-amp amplifies the input signal. It is defined as the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
| Gain (A) | = | Output Voltage (Vout) | / | Input Voltage (Vin) |
|---|
It is important to note that the gain of an op-amp is typically very high, often in the range of tens of thousands or even millions. This high gain makes op-amps versatile and widely used in various electronic circuits.
Types of Op Amp Gain
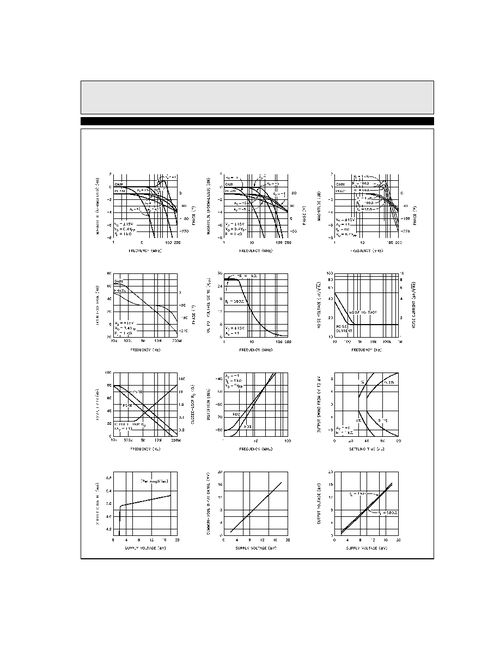
There are two main types of op amp gain: open-loop gain and closed-loop gain.
Open-Loop Gain
Open-loop gain refers to the gain of an op-amp when it is not used in a feedback configuration. In this case, the gain is very high, as mentioned earlier. However, using an op-amp in an open-loop configuration is not practical, as it can lead to instability and noise issues.
Closed-Loop Gain
Closed-loop gain, on the other hand, is the gain of an op-amp when it is used in a feedback configuration. This type of gain is much lower than the open-loop gain and is more practical for real-world applications. The closed-loop gain can be calculated using the following formula:
| Closed-Loop Gain (Acl) | = | Aol (1 + Z1/Z2) |
|---|
Where Aol is the open-loop gain, and Z1 and Z2 are the feedback and input impedance, respectively.
Calculating Op Amp Gain
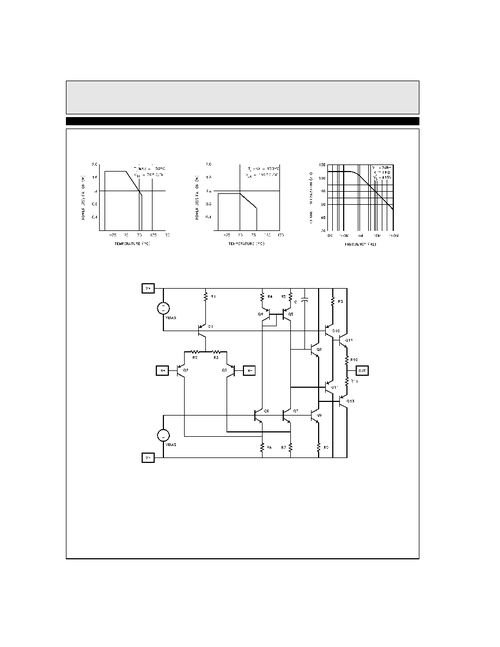
Calculating the gain of an op-amp can be done using various methods, depending on the circuit configuration. Here are some common methods:
Using the Voltage Divider Rule
The voltage divider rule can be used to calculate the gain of an inverting amplifier. In this configuration, the gain is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (R2) to the input resistor (R1):
| Gain (A) | = | -R2/R1 |
|---|
Using the Op Amp Gain Formula
The op amp gain formula can be used to calculate the gain of any op-amp circuit. The formula is:
| Gain (A) | = | Aol (1 + Z1/Z2) |
|---|
Practical Applications of Op Amp Gain
Op amp gain has numerous practical applications in electronic circuits. Here are some of the most common ones:
Signal Amplification
One of the primary applications of op amp gain is signal amplification. Op-amps can be used to amplify weak signals, making them suitable for various applications, such as audio amplifiers, radio frequency (RF) amplifiers, and sensor signal conditioning.








